Graphite Schist
Hello Friday! Hello #DignayanBiyernes!
This week we feature a metamorphic rock specifically called graphite schist. Find out below how it differs from other schists we posted before.
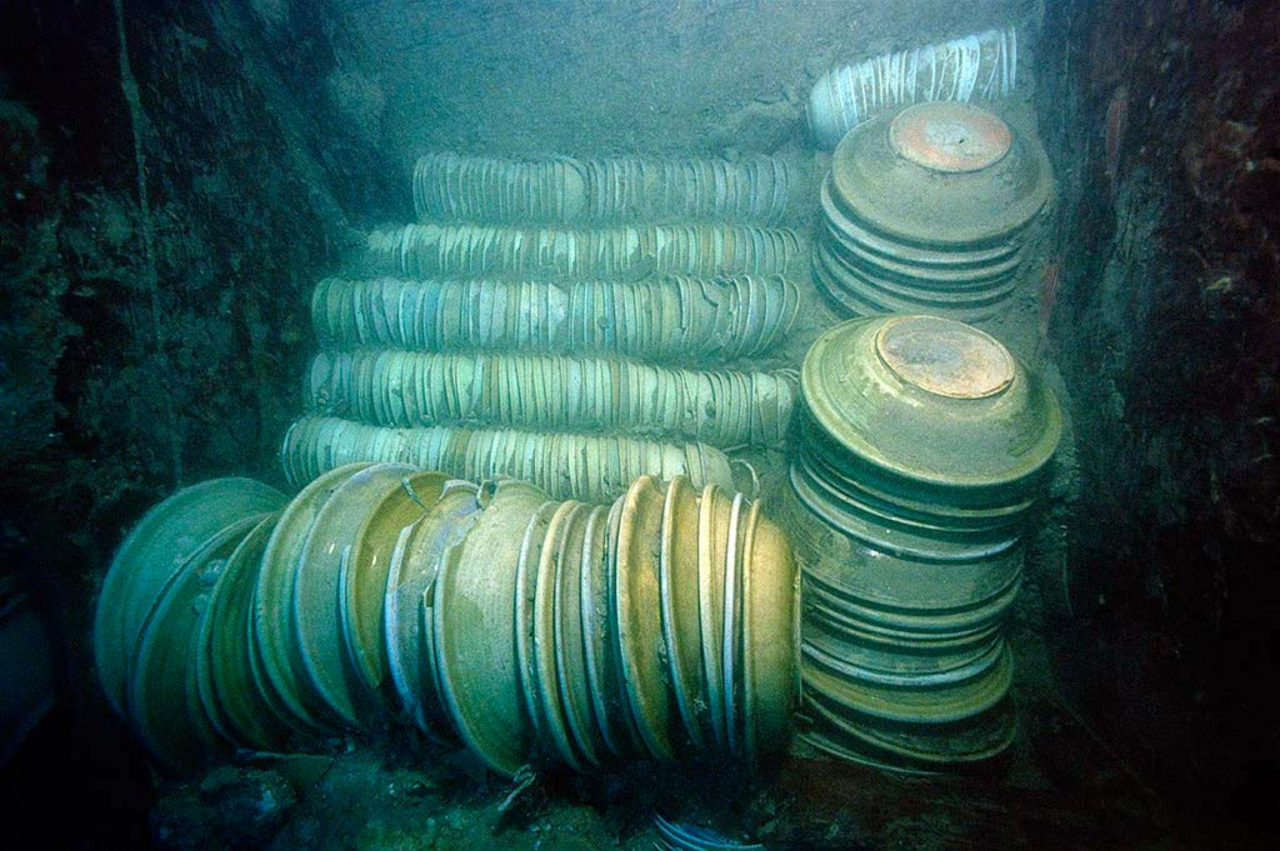
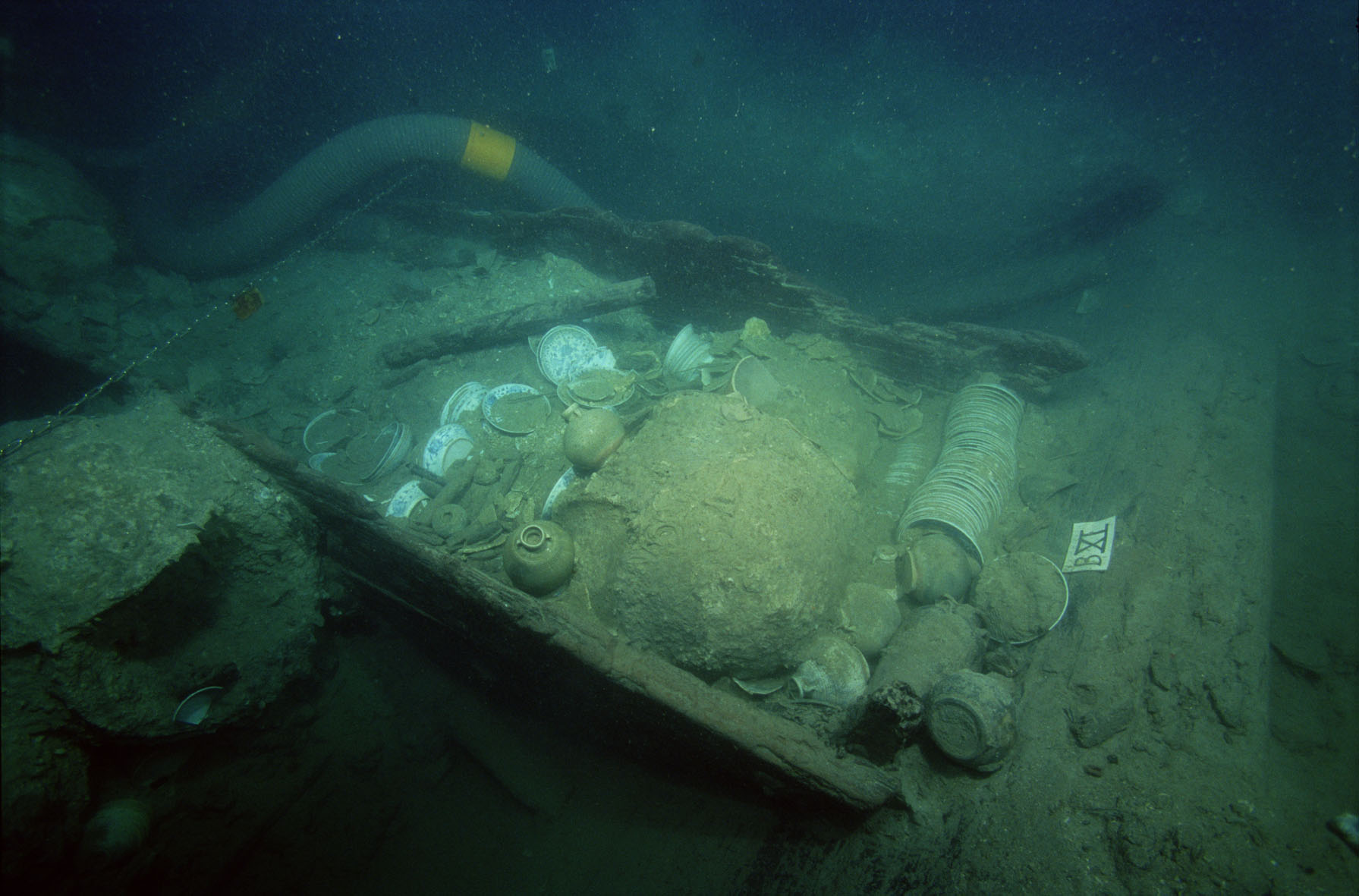
Schists are metamorphic rocks whose minerals are arranged in such a way that they would fragment into thin plates or flakes. This is called schistosity. Typically, schist is composed of flat platy minerals like mica, talc, chlorite, and graphite. In samples where graphite is the most abundant or the dominant mineral present, the schist is more properly identified as graphite schist. Graphite is a mineral consisting of carbon and is usually iron black to steel grey. This is also the dominant color for graphite schists.
The specimen featured here was collected from San Vicente, Palawan by the Geology and Paleontology Division of the #NationalMuseumPH in 2015. This metamorphic rock belongs to the Cretaceous (145-66 million years old) Caramay Schist which is one of the oldest rock formations in Palawan. Fresh rock samples of this specimen have a sub-metallic luster but weathered samples appear silver gray. An analysis of its composition and structure very much suggests that it was once a sedimentary rock a very long time ago. Graphite schists in this locality were observed to form layers with varying thickness, ranging from less than 1 cm to tens of meters thick.
Your National Museum of Natural History and all museums at the NMP Complex are now welcoming guests of all ages. Book your tour now through this website.
#MuseumFromHome
Text and image by the NMP Geology and Paleontology Division
© National Museum of the Philippines (2021)









 Owing to its survival of the destruction of the Battle of Manila in 1945 and all the numerous calamities that came before and after it that shook the capital to its foundations, the
Owing to its survival of the destruction of the Battle of Manila in 1945 and all the numerous calamities that came before and after it that shook the capital to its foundations, the 










